HA Special Sands
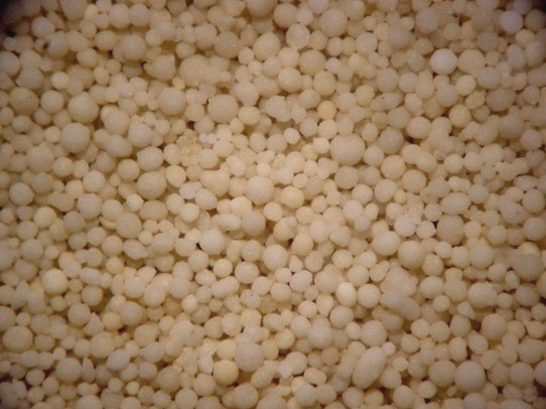
The term “special sand” covers all industrial minerals (except quartz sand) commonly used in foundries as moulding material for the manufacture of cores and moulds/dies.
Special sands include natural mineral sands, sintering and melting products produced in granular form or turned into granular form by breaking, grinding and grading processes, or inorganic mineral sands produced by other physical-chemical methods.
Special sands are different from quartz sand, particularly as regards their significantly lower thermal expansion behaviour within the temperature range of 20 – 600°C, their heat conductivity, refractoriness, and other physical characteristics.
Strengths of HA special sands
Special sands are used instead of quartz sand for coremaking and mouldmaking because they are characterized by better physical-chemical properties.
In consideration of the casting properties to be achieved, the individual advantages of a special sand can be used to:
- avoid sand expansion defects, especially finning/veining
- avoid the addition of gas-forming ingredients
reduce the core weight
avoid metal penetration
- increase the flowability of the sand
avoid a mould-metal interface reaction
control the formation of microstructure
produce thin-walled castings
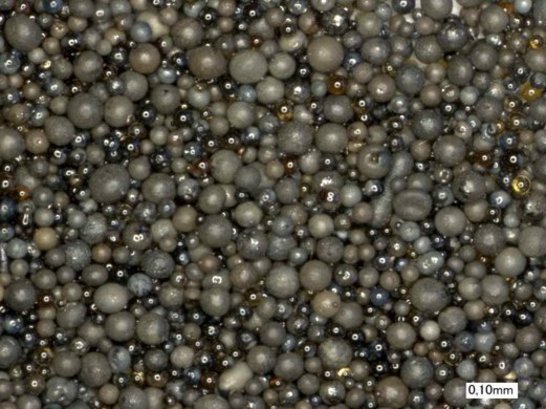
Chromite Sand
Chromite sand is used for its high thermal resistance, fast chilling capacity and resistance to liquid metal penetration.
Its thermal expansion is uniform and clearly lower than that of silica sand thus finning problems are minimised.
Chromite sand is provided with a size of 45 - 65 AFA and a typical composition of Cr2O3: 46%, FeO: 27%, Al2O3: 15% and MgO:10%.
It is compatible with all binding systems and steel castings, being specially appropriate for chromium, chromium-nickel and manganese steel casting.
When compared to silica sand, it is less reactive with MnO thus calcination problems are reduced.
The chromite sand is compatible with all chemical processes for molds and cores. Currently large amounts of chromite sand are used in the foundry industry for the manufacture of molds and cores.
Chromite Sand is applicable to all types of steels and very appropriate for parts of chrome, chrome-nickel, manganese steel.
The Chromite Sand, has the advantage over silica sand that is less reactive with the manganese oxide, reducing, thus, the calcination problems.

Olivine
Olivine special sand is available in different sizes and is particularly appropriate for mould and coremaking.
Its inherent alkalinity makes it applicable in manganese steel casting, being less reactive with MnO than silica sand.
Olivine sand thermal expansion is lower than that of silica sand and its high thermal shock resistance furthermore reduces sand expansion problems.
Foundry quality is supplied with 50–60 AFA size and typical composition is MgO: 48%, SiO2: 41% and Fe2O3: 8%.
Granulated olivine of 2-6 mm is used in the iron and steel industry as taphole filler in bottom (EBT and OBT) and lateral electric furnaces.
SiO2 in sand is not free but combined as magnesium orthosilicate (Mg2SiO4) which ensures minimal steel silicon uptake.
Olivine sand with 100–120 AFA size is used as raw material in the refractory industry for gunite manufacturing ultimately applied in the iron and steel industry.
The strengths of Cerabeads
- Suitable for all types of castings
- Suitable for the following processes: PUR-Cold-Box, SO2-Cold-Box, shell moulding, cold resin, resole-CO2 /MF, resole/ester
- Low coefficient of linear expansion
- Ideally suited for extreme thermal stress
- Optional selection of the ideal classification for your specific applications
The main difference between HA special sands and silica sand is the significantly lower coefficient of linear expansion and significantly lower thermal expansion behaviour during the casting process.
Furthermore, HA special sands are the ideal moulding material for core production:
- High sintering and melting points (except J-sand)
- Compatibility with all binders used for core production
- High cold-strength properties of the moulding material
- High hot strength properties of the moulding material (except J-sand)
- Available in a range of different classifications
Many years of experience at Hüttenes-Albertus have shown that the use of HA special sands depends on the complexity of the respective casting, the metal used for the casting, the susceptibility to veining, the casting temperature and the binder system.
Application examples
The use of J-sand for PUR Cold-Box core production allows automotive series castings to be produced without sand expansion defects, thereby avoiding the need to add gas and odour-forming additives.
For castings manufactured under extreme thermal stresses with a high tendency to veining, we recommend the use of Kerphalite KF, Cerabeads or M-Sand for PUR-Cold-Box. The high-temperature properties of these HA special sands also ensure that they can be used as a basic moulding material for steel castings.
The thermal expansion of shell moulding material tends towards zero when using quartz-special sand mixtures. When using 100% Kerphalite KF and Cerabeads, shrinkage of the shell core occurs. In sensitive hydraulic and automotive casting, complex cores are produced with coated HA special sands, which guarantee flawless castings close to final dimensions.
Hüttenes-Albertus markets its shell moulding sands containing Cerabeads under the brand name Keracron®.